04/06/2021
Extraction de blessé: L'avenir
12/04/2021
KIA pour les UK en Afghanistan
Killed in action (KIA): an analysis of military personnel who died of their injuries before reaching a definitive medical treatment facility in Afghanistan (2004-2014)
Introduction: The majority of combat deaths occur before arrival at a medical treatment facility but no previous studies have comprehensively examined this phase of care.
Methods: The UK Joint Theatre Trauma Registry was used to identify all UK military personnel who died in Afghanistan (2004-2014). These data were linked to non-medical tactical and operational records to provide an accurate timeline of events. Cause of death was determined from records taken at postmortem review. The primary objective was to report time between injury and death in those killed in action (KIA); secondary objectives included: reporting mortality at key North Atlantic Treaty Organisation timelines (0, 10, 60, 120 min), comparison of temporal lethality for different anatomical injuries and analysing trends in the case fatality rate (CFR).
Results: 2413 UK personnel were injured in Afghanistan from 2004 to 2014; 448 died, with a CFR of 18.6%. 390 (87.1%) of these died prehospital (n=348 KIA, n=42 killed non-enemy action). Complete data were available for n=303 (87.1%) KIA: median Injury Severity Score 75.0 (IQR 55.5-75.0). The predominant mechanisms were improvised explosive device (n=166, 54.8%) and gunshot wound (n=96, 31.7%).In the KIA cohort, the median time to death was 0.0 (IQR 0.0-21.8) min; 173 (57.1%) died immediately (0 min). At 10, 60 and 120 min post injury, 205 (67.7%), 277 (91.4%) and 300 (99.0%) casualties were dead, respectively.

Whole body primary injury had the fastest mortality. Overall prehospital CFR improved throughout the period while in-hospital CFR remained constant.
Conclusion: Over two-thirds of KIA deaths occurred within 10 min of injury. Improvement in the CFR in Afghanistan was predominantly in the prehospital phase.
06/04/2021
Inexpérimenté mais sûr de soi ! Constat alarmant
Inexperienced but Confident: A Survey of Advanced Life Support Providers and Life-saving Interventions in the Israel Defense Forces
Haddad N et Al. Military Medicine, Volume 186, Issue Supplement_1, January-February 2021,
----------------------------------------------------
Suivre une formation ne veut pas dire savoir faire. Il est impératif de VÉRIFIER le savoir faire
----------------------------------------------------
Objective:
The objective of this study was to assess the current experience of Israel Defense Forces' (IDF) advanced life support (ALS) providers in performing life-saving interventions (LSIs), the rate of doctors and paramedics achieving the Trauma and Combat Medicine Branch benchmarks, and the rate of providers feeling confident in performing the interventions although not achieving the benchmarks.
Methods:
This study was based on an online survey delivered to IDF ALS providers. The survey investigated demographics; experience in performing endotracheal intubation, cricothyroidotomy, tube thoracostomy, and intraosseous access on human patients; and confidence in performing these LSIs. All benchmarks chosen referred to the number of times performed in the previous year. The benchmarks were 20 for intubation, 3 for cricothyroidotomy, 4 for tube thoracostomy, and 3 for intraosseous access.
Results:
During the survey period, 175 IDF ALS providers started the survey, but only 138 (79%) completed it, 93 (67%) of them were paramedics. Doctors had higher rates than paramedics of failing to achieve the benchmarks for intubation (96 vs. 57%, P < .001) and intraosseous access (100 vs. 66%, P < .001). All respondents failed to achieve the benchmark for cricothyroidotomy, and all but one paramedic failed to achieve the tube thoracostomy benchmark. Doctors had lower rates of high confidence when failing to achieve the benchmark for intubation (35 vs. 64%, P = .008) and intraosseous access (7 vs. 31%, P = .005) compared to paramedics.
Conclusion:
IDF ALS providers have alarmingly limited experience in performing LSIs. Many of them are confident in their ability despite not achieving evidence-based benchmarks. Additional training is required, maybe as a part of an annual medical fitness test.
05/02/2021
Stage de préparation OPEX ?: Insuffisant !
Introduction:
Military-Civilian partnerships (MCPs), such as the Navy Trauma Training Center, are an essential tool for training military trauma care providers. Despite Congressional and military leadership support, sparse data exist to quantify participants' clinical opportunities in MCPs. These preliminary data from an ongoing Navy Trauma Training Center outcomes study quantify clinical experiences and compare skill observation to skill performance.
Materials and methods:
Participants completed clinical logs after each patient encounter to quantify both patients and procedures they were involved with during clinical rotations; they self-reported demographic data. Data analyses included descriptive statistics and chi-square statistics to compare skills observed to skills performed between the first and second half of the 21-day course.
Results:
A sample of 47 Navy personnel (30 corpsmen, 10 nurses, 3 physician assistants, 4 physicians) completed 551 clinical logs. Most logs (453/551) reflected experiences in the emergency department, where corpsmen and nurses each spent 102.0 hours, and physician assistants and physicians each spent 105.4 hours. Logs completed per participant ranged from 1 to 31, (mean = 8). No professional group was more likely than others to complete the clinical logs. Completion rates varied by cohort, both overall and by clinical role. Of emergency department logs, 39% reflected highest acuity patients, compared with 21% of intensive care unit logs, and 61% of operating room logs. Penetrating trauma was reported on 16.5% of logs. Primary and secondary trauma assessments were the most commonly reported clinical opportunities, followed by obtaining intravenous access and administration of analgesic medications. With few exceptions, logs reflected skill observation versus skill performance, a ratio that did not change over time.
Conclusion:
Prospective real-time data of actual clinical activity is a crucial measure of the success of MCPs. These preliminary data provide a beginning perspective on how these experiences contribute to maintaining a skilled military medical force.
09/12/2020
ATLS: Pas suffisant à la guerre
Time to Update Army Medical Doctrine
Knight RM et Al. et Al. Mil Med . 2020 Dec 3;usaa540
Une analyse de l'organisation US qui pointe la nécessité actuelle de réorganiser la prise en charge des blessés de guerre par des équipes formées et entraînées aux techniques de réanimation de l'avant. Cette analyse pointe du doigt l'inadapttaion des roles 1, l'importance des medevac et l'inadéquation de l'ATLS au combat moderne.
27/11/2020
Trauma du larynx: Faites une échographie !
Novel role of focused airway ultrasound in early airway assessment of suspected laryngeal trauma
Adi et al. Ultrasound J (2020) 12:37
Case presentation
We report a case series that illustrate the diagnostic value of focused airway ultrasound in the diagnosis of laryngeal trauma in patients presenting with blunt neck injury.
Conclusion
Early recognition, appropriate triaging, accurate airway evaluation, and prompt management of such injuries are essential. In this case series, we introduce the potential role of focused airway ultrasound in suspected laryngeal trauma, and the correlation of these exam findings with that of computed tomography (CT) scanning, based on the Schaefer classification of laryngeal injury.
23/11/2020
Médicine tactique: Apport de la période afghane
Evolution of Pararescue medicine during operation Enduring Freedom
Stephen Rush S. et Al. Mil Med . 2015 Mar;180(3 Suppl):68-73.
This article highlights recent advances made in U.S. Air Force Pararescue Medical Operations in relation to tactical evacuation procedures. Most of these changes have been adopted and adapted from civilian medicine practice, and some have come from shared experiences with partner nations. Patient assessment includes a more comprehensive evaluation for hemorrhage and indications for hemorrhagic control. Ketamine has replaced morphine and fentanyl as the primary sedative used during rapid sequence intubation and procedural sedation. There has been an increasing use of the bougie to clear an airway or nasal cavity that becomes packed with debris. Video laryngoscopy provides advantages over direct laryngoscopy, especially in situations where there are environmental constraints such as the back of a Pave Hawk helicopter. Intraosseous access has become popular to treat and control hemorrhagic shock when peripheral intravenous access is impractical or impossible. Revisions to patient treatment cards have improved the efficacy and compliance of documentation and have made patient handoff more efficient. These improvements have only been possible because of the concerted efforts of U.S. Air Force and partner platforms operating in Afghanistan.
11/11/2020
Plasma préhospitalier. Surtout pour certains
Characterization of unexpected survivors following a prehospital plasma randomized trial
J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2020 Nov;89(5):908-914
Background: Prehospital plasma improves survival for severely injured trauma patients transported by air ambulance. We sought to characterize the unexpected survivors, patients who survived despite having high predicted mortality after traumatic injury.
Methods: The Prehospital Air Medical Plasma trial randomized severely injured patients (n = 501) to receive either standard care (crystalloid) or two units of prehospital plasma followed by standard care fluid resuscitation. We built a generalized linear model to estimate patient mortality. Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was used to evaluate model performance. We defined unexpected survivors as patients who had a predicted mortality greater than 50% and survived to 30 days. We characterized patient demographics, clinical features, and outcomes of the unexpected survivors. Observed to expected (O/E) ratios and Z-statistics were calculated using model-estimated mortality for each cohort.
Results: Our model predicted mortality better than Injury Severity Score or Revised Trauma Score parameters and identified 36 unexpected survivors. Compared with expected survivors, unexpected survivors were younger (33 years [24, 52 years] vs. 47 years [32, 59 years], p = 0.013), were more severely injured (Injury Severity Score 34 [22, 50] vs. 18 [10, 27], p < 0.001), had worse organ dysfunction and hospital resource outcomes (multiple organ failure, intensive care unit, hospital length of stay, and ventilator days), and were more likely to receive prehospital plasma (67 vs. 46%, p = 0.031).
Nonsurvivors with high predicted mortality were more likely to receive standard care resuscitation (p < 0.001). Unexpected survivors who received prehospital plasma had a lower observed to expected mortality than those that received standard care resuscitation (O/E 0.56 [0.33-0.84] vs. 1.0 [0.73-1.32]). The number of prehospital plasma survivors (24) exceeded the number of predicted survivors (n = 10) estimated by our model (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Prehospital plasma is associated with an increase in the number of unexpected survivors following severe traumatic injury. Prehospital interventions may improve the probability of survival for injured patients with high predicted mortality based on early injury characteristics, vital signs, and resuscitation measures.
09/02/2020
Tuerie de masse ou violence urbaine: Vite vers l'hôpital !
Comparison of the causes of death and wounding patterns in urban firearm-related violence and civilian public mass shooting events.
BACKGROUND:
There are no reports comparing wounding pattern in urban and public mass shooting events (CPMS). Because CPMS receive greater media coverage, there is a connation that the nature of wounding is more grave than daily urban gun violence. We hypothesize that the mechanism of death following urban gunshot wounds (GSWs) is the same as has been reported following CPMS.
METHODS:
Autopsy reports of all firearm-related deaths in Washington, DC were reviewed from January 1, 2016, to December 31, 2017. Demographic data, firearm type, number and anatomic location of GSWs, and organ(s) injured were abstracted. The organ injury resulting in death was noted. The results were compared with a previously published study of 19 CPMS events involving 213 victims.
RESULTS:
One hundred eighty-six urban autopsy reports were reviewed. There were 171 (92%) homicides and 13 (7%) suicides. Handguns were implicated in 180 (97%) events. One hundred eight (59%) gunshots were to the chest/upper back, 85 (46%) to the head, 77 (42%) to an extremity, and 71 (38%) to the abdomen/lower back. The leading mechanisms of death in both urban firearm violence and CPMS were injury to the brain, lung parenchyma, and heart. Fatal brain injury was more common in CPMS events as compared with urban events involving a handgun.
CONCLUSION:
There is little difference in wounding pattern between urban and CPMS firearm events. Based on the organs injured, rapid point of wounding care and transport to a trauma center remain the best options for mitigating death following all GSW events.
17/01/2020
RECO SFAR Traumatismes abdominaux
10/01/2020
Plaie du coeur: Un retex brestois
24/10/2019
Trauma airways: Une revue
Airway trauma: a review on epidemiology, mechanisms of injury, diagnosis and treatment.
Prokakis C et Al. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2014 Jun 30;9:117.
Airway injuries are life threatening conditions. A very little number of patients suffering air injuries are transferred live at the hospital. The diagnosis requires a high index of suspicion based on the presence of non-specific for these injuries symptoms and signs and a thorough knowledge of the mechanisms of injury. Bronchoscopy and chest computed tomography with MPR and 3D reconstruction of the airway represent the procedures of choice for the definitive diagnosis. Endotracheal intubation under bronchoscopic guidance is the key point to gain airway control and appropriate ventilation. Primary repair with direct suture or resection and an end to end anastomosis is the treatment of choice for patients suffering from tracheobronchial injuries (TBI). The surgical approach to the injured airway depends on its location. Selected patients, mainly with iatrogenic injuries, can be treated conservatively as long as the injury is small (<2 cm), a secure and patent airway and adequate ventilation are achieved, and there are no signs of sepsis. Patients with delayed presentation airway injuries should be referred for surgical treatment. Intraoperative evaluation of the viability of the lung parenchyma beyond the site of stenosis/obstruction is mandatory to avoid unnecessary lung resection.
| Tags : airway
17/09/2019
Violences urbaines et tueries massives: Des profils proches ?
Comparison of the Causes of Death and Wounding Patterns in Urban Firearm-Related Violence and Civilian Public Mass Shooting Events.
BACKGROUND:
There are no reports comparing wounding pattern in urban and public mass shooting events (CPMS). Because CPMS receive greater media coverage, there is a connation that the nature of wounding is more grave than daily urban gun violence. We hypothesize that the mechanism of death following urban GSWs is the same as has been reported following CPMS.
METHODS:
Autopsy reports of all firearm related deaths in Washington, DC were reviewed from January 1, 2016 to December 31, 2017. Demographic data, firearm type, number and anatomic location of GSWs, and organ(s) injured were abstracted. The organ injury resulting in death was noted. The results were compared to a previously published study of 19 CPMS events involving 213 victims.
RESULTS:
186 urban autopsy reports were reviewed. There were 171 (92%) homicides and 13 (7%) suicides. Handguns were implicated in 180 (97%) events. One hundred eight gunshots (59%) were to the chest/upper back, 85 (46%) to the head, 77 (42%) to an extremity, and 71 (38%) to the abdomen/lower back. The leading mechanisms of death in both urban firearm violence and CPMS were injury to the brain, lung parenchyma, and heart. Fatal brain injury was more common in CPMS events as compared to urban events involving a handgun.
CONCLUSION:
There is little difference in wounding pattern between urban and CPMS firearm events. Based on the organs injured, rapid point of wounding care and transport to a trauma center remain the best options for mitigating death following all GSW events.
08/09/2019
Lactates en préhospitalier: Oui
Prognostic value of lactate in prehospital care as a predictor of early mortality.
----------------------------
Les outils d'aideau diagnostic comme l'échographie tendent à devenir d'emploi routinier en préhospitalier. Le dosage des lactates fait partie de ces outils.
----------------------------
BACKGROUND:
Prehospital Emergency Medical Services must attend to patients with complex physiopathological situations with little data and in the shortest possible time. The objective of this work was to study lactic acid values and their usefulness in the prehospital setting to help in clinical decision-making.
STUDY DESIGN:
We conducted a longitudinal prospective, observational study on patients over 18 years of age who, after being evaluated by the Advanced Life Support Unit, were taken to the hospital between April and June 2018. We analyzed demographic variables, prehospital lactic acid values and early mortality (<30 days). The area under the curve of the receiver operating characteristic was calculated for the prehospital value of lactic acid.
RESULTS:
A total of 279 patients were included in our study. The median age was 68 years (interquartile range: 54-80 years). Overall 30-day mortality was 9% (25 patients). The area under the curve for lactic acid to predict overall mortality at 30 days of care was 0.82 (95% CI: 0.76-0.89).
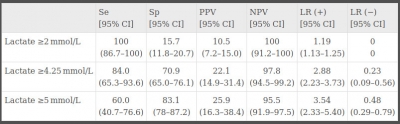
The lactate value with the best sensitivity and specificity overall was 4.25 mmol/L with a sensitivity of 84% (95% CI: 65.3-93.6) and specificity of 70% (95% CI: 65.0-76.1).
CONCLUSIONS:
The level of lactic acid can be a complementary tool in the field of prehospital emergencies that will guide us early in the detection of critical patients.
24/04/2019
Numéro special THOR
16/04/2019
FST, chirurgie et USAparticulièrement innovant
TCCC: Un écosystème spécifique
Un regard sur l'émergence des nouvelles modalités de prise en charge des blessés de guerre avec pour point d'orgue l'innovation conduite et la construction d'un écosystème complet autour de la prise en charge du blessé de guerre. Une démarche à comprendre et à bien méditer.
Clic sur l'image pour accéder au document
10/04/2019
Saignements majeurs: 5ème révision EU
19/03/2019
ATLS 9ème Edition
16/03/2019
Irak/Syrie: Quelle activité ?
The First 30 Months Experience in the Non-Doctrinal Operation Inherent Resolve Medical Theater
Schauer SG et Al. Mil Med. 2018 Nov 5. doi: 10.1093/milmed/usy273
----------------------------------------------------
Les auteurs rapportent le soutien médical de combats menés essentiellement par des troupes amies. La lecture des fichiers associés à la publication s'impose. Pose de garrot et réchauffement sont les gestes préhospitaliers les plus fréquents. Il faut noter, au niveau des structures chirurgicales la fréquence des drainages thoraciques, des intubations et des laparotomies.
----------------------------------------------------
Introduction:
U.S. military forces were redeployed in 2014 in support of Operation Inherent Resolve (OIR), operating in an austere theater without the benefit of an established medical system. We seek to describe the prehospital and hospital-based care delivered in this medically immature, non-doctrinal theater.
Materials and Methods:
We queried the Department of Defense Trauma Registry (DODTR) for all encounters associated with OIR from August 2014 through June 2017. We sought all available prehospital and hospital-based data.
Results:
There were a total of 826 adults that met inclusion; 816 were from Iraq and the remaining 10 were from Syria. The median age was 21 years and the most frequent mechanism of injury was explosives (47.7%). Median composite injury severity scores were low (9, IQR 2.75-14) and the most frequent seriously injured body region was the extremities (23.0%). Most subjects (94.9%) survived to hospital discharge. Open fractures were the most frequent major injury (26.0%). In the prehospital setting, opioids were the most frequently administered medication (9.3%) and warming blanket application (48.7%) and intravenous line placement (24.8%) were the most frequent interventions. In the emergency department, Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma exams (64.3%) was the most frequently performed study and endotracheal intubations were the most frequent (29.9%) procedure. In the operating room, the most frequently performed procedure was exploratory laparotomy (12.3%).
Conclusions:
Host nation military males injured by explosion comprised the majority of casualties. Open fracture was the most common major injury. Hence, future research should focus upon the unique challenges of delivering care to members of partner forces with particular focus upon interventions to optimize outcomes among patients sustaining open fractures.