02/04/2024
Les gestes US du Role 1 chez les américains
An Analysis of 13 Years of Prehospital Combat Casualty Care: Implications for Maintaining a Ready Medical Force
Schauer SG et Al. Prehosp Emerg Care. 2022 May-Jun;26(3):370-379.
----------------------------------
Des choses simples dans un contexte où les medevac étaient très rapides, ce qui n'est plus le cas. Poser des garrots est toujours nécessaires MAIS ne suffit plus. Les gestes sophistiqués de réanimation doivent absolument être maîtrisées. Cela passe par une autre vision, que celle actuelle, de la médicalisation de l'avant.
----------------------------------
Background:
Most potentially preventable deaths occur in the prehospital setting before reaching a military treatment facility with surgical capabilities. Thus, optimizing the care we deliver in the prehospital combat setting represents a ripe target for reducing mortality. We sought to analyze prehospital data within the Department of Defense Trauma Registry (DODTR).
Materials and methods:
We requested all encounters with any prehospital activity (e.g., interventions, transportation, vital signs) documented within the DODTR from January 2007 to March 2020 along with all hospital-based data that was available. We excluded from our search casualties that had no prehospital activity documented.
Results:
There were 28,950 encounters that met inclusion criteria. Of these, 25,897 (89.5%) were adults and 3053 were children (10.5%). There was a steady decline in the number of casualties encountered with the most notable decline occurring in 2014. U.S. military casualties comprised the largest proportion (n = 10,182) of subjects followed by host nation civilians (n = 9637). The median age was 24 years (interquartile range/IQR 21-29).
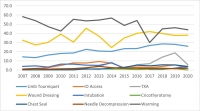
Most were battle injuries (78.6%) and part of Operation ENDURING FREEDOM (61.8%) and Operation IRAQI FREEDOM (24.4%). Most sustained injuries from explosives (52.1%) followed by firearms (28.1%), with serious injury to the extremities (24.9%) occurring most frequently. The median injury severity score was 9 (IQR 4-16) with most surviving to discharge (95.0%). A minority had a documented medic or combat lifesaver (27.9%) in their chain of care, nor did they pass through an aid station (3.0%). Air evacuation predominated (77.9%).
Conclusions:
Within our dataset, the deployed U.S. military medical system provided prehospital medical care to at least 28,950 combat casualties consisting mostly of U.S. military personnel and host nation civilian care. There was a rapid decline in combat casualty volumes since 2014, however, on a per-encounter basis there was no apparent drop in procedural volume.
15/03/2024
Plus d'infirmiers spécialisés dans le trauma
Une évidence. Et dans le système français le modèle de cet infirmier est un IADE
ACNPs in the U.S. Army-Medical Force Multipliers for Large-Scale Combat Operations
07/12/2023
Histoires de conversion du garrot
Rethinking limb tourniquet conversion in the prehospital environment
John B Holcomb JB et Al. J Trauma Acute Care Surg . 2023 Dec 1;95(6):e54-e60.
----------------------------------------
Un plaidoyer pour un emploi large MAIS raisonné qui doit être ENSEIGNE et notamment la problématique de sa conversion. Ceci est d'autant plus important que les délais d'évacuations risquent d'être longs.
----------------------------------------
We have highlighted the issue of overuse of tourniquets and described why tourniquet conversion and replacement should be taught and done in the prehospital setting.
Clic sur l'image pour accéder au document
01/12/2023
Military Medicine
20/11/2023
Les anesthésistes: Pièce importante dans les guerres hybrides
A Gray Future: The Role of the Anesthesiologist in Hybrid Warfare
Granholm F et Al. Anesthesiology. 2023 Nov 1;139(5):563-567.
During the last few decades, the increasing use of asymmetric and multimodal tactics by terrorists has led anesthesiologists worldwide to analyze and discuss their role in mass casualty scenarios in more depth. Now anesthesiologists must address the new situation of hybrid threats and hybrid warfare. This will have a direct impact on anesthesiology and intensive care, and in the end, the health and well-being of critical patients of all ages. To be able to respond to a hybrid threat efficiently and effectively, it is imperative that anesthesiologists play an early and integral role in mitigation and response planning.
24/10/2023
Chirurgie à l'avant. L'histoire enseigne de petites structures proches des combats
Surgery on the battlefield: Mobile surgical units in the Second World War and the memoirs they produced
Venables KM J Med Biogr. 2023 Aug; 31(3): 202–211.
In the Second World War, there was a flowering of the battlefield surgery pioneered in the Spanish Civil War. There were small, mobile surgical units in all the theatres of the War, working close behind the fighting and deployed flexibly according to the nature of the conflict. With equipment transported by truck, jeep or mule, they operated in tents, bunkers and requisitioned buildings and carried out abdominal, thoracic, head and neck, and limb surgery. Their role was to save life and to ensure that wounded soldiers were stable for casualty evacuation back down the line to a base hospital.

There is a handful of memoirs by British doctors who worked in these units and they make enthralling reading. Casualty evacuation by air replaced the use of mobile surgical units in later wars, throwing into doubt their future relevance in the management of battle wounds. But recent re-evaluations by military planners suggest that their mobility still gives them a place, so the wartime memoirs may have more value than simply as war stories.
19/01/2023
Le drone: Incontournable !
Drones reduce the treatment-free interval in search and rescue operations with telemedical support – A randomized control trial
Van Veelen MJ et Al. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2023.01.020
------------------------------------
Un outil sans nul doute à maîtriser à la lumière des événements ukrainiens
------------------------------------
Introduction
Response to medical incidents in mountainous areas is delayed due to the remote and challenging terrain. Drones could assist in a quicker search for patients and can facilitate earlier treatment through delivery of medical equipment. We aim to assess the effects of drone deployment in search and rescue (SAR) operations in challenging terrain. We hypothesize that drones can reduce the search time and treatment-free interval of patients through initiation of telemedicine in a single mission.
Methods
In this randomized control trial with a cross-over design two methods of searching for and initiating treatment of a patient were compared. The primary outcome was a comparison of the times for locating a patient through visual contact and starting treatment on-site between the drone assisted intervention arm and the conventional ground rescue control arm. A linear mixed model (LMM) was used to evaluate the effect of using a drone on search and start of treatment times.
Results
Twenty-four SAR missions, performed by six SAR teams each with four team members, were analyzed. The mean time to locate the patient was 14.6 min (95% CI 11.3–17.9) in the drone assisted intervention arm and 20.6 min (95% CI 17.3–23.9) in the control arm. The mean time to start treatment was 15.7 min (95% CI 12.4–19.0) in the drone assisted arm and 22.4 min (95% CI 19.1–25.7) in the control arm ( p < 0.01 for both comparisons).

Conclusion
Drone deployment in SAR operations leads to a reduction in search time and treatment-free interval of patients in challenging terrain, which could improve outcomes in patients suffering from traumatic injuries, the most commonly occurring incident requiring mountain rescue deployment.
| Tags : drone
23/10/2022
Drone: Pour quoi faire ?
| Tags : drone
05/07/2022
Risques biologiques émergents: Etre prêts ?
A Hierarchy of Medical Countermeasures Against Biological Threats
08/06/2022
Trauma Prehospitalier: Aides
| Tags : traumatologie
14/03/2021
Hydrazine: Qu'est ce que c'est ?
The Toxicity, Pathophysiology, and Treatment of Acute Hydrazine Propellant Exposure: A Systematic Review
Nguyen HN et Al. Mil Med. 2021 Feb 26;186(3-4):e319-e326.
-----------------------------------
L'hydrazine est employé comme combustible dans les fusées et dans les F16 américains en tant que combustible alimentant une unité de puissance de secours. Et cela n'est pas sans conséquence lors d'une intervention auprès d'un tel type d'aéronef.
-----------------------------------
Introduction:
Hydrazines are highly toxic inorganic liquids that are used as propellants in military and aviation industries, such as the U.S. Air Force F-16 Emergency Power Unit and SpaceX SuperDraco Rockets. The most commonly used derivatives include hydrazine, monomethylhydrazine, and 1,1-dimethylhydrazine (unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine). Industrial workers in close contact with hydrazines during routine maintenance tasks can be exposed to levels well above the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health relative exposure limits.
Materials and methods: A systematic review was performed using PubMed, Web of Science, Google Scholar, National Aeronautics and Space Administration Technical Server, and Defense Technical Information Center, and data related to hydrazine exposures were searched from inception to April 2020. Publications or reports addressing hydrazine toxicity, pathophysiology, and treatment of hydrazine fuel exposure were selected.
Results: Acute toxic exposures to hydrazine and its derivatives are rare. There are few case reports of acute toxic exposure in humans, and data are largely based on animal studies. The initial search identified 741 articles, manuscripts, and government reports. After screening for eligibility, 51 were included in this review. Eight articles reported acute exposures to hydrazine propellant in humans, and an additional 14 articles reported relevant animal data.
Conclusions: Exposure to small amounts of hydrazine and its derivatives can cause significant soft tissue injury, pulmonary injury, seizures, coma, and death. Neurologic presentations can vary based on exposure compound and dose. Decontamination is critical as treatment is mainly supportive. High-dose intravenous pyridoxine has been suggested as treatment for hydrazine-related neurologic toxicity, but this recommendation is based on limited human data. Despite recent research efforts to generate less toxic alternatives to hydrazine fuel, it will likely continue to have a role in military and aviation industries. Aerospace and military physicians should be aware of the toxicity associated with hydrazine exposure and be prepared to treat hydrazine toxicity in at-risk populations.
10/01/2020
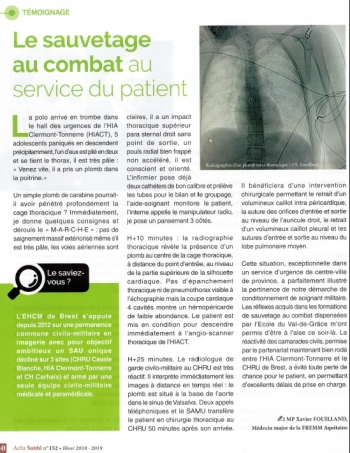
Plaie du coeur: Un retex brestois
03/01/2020
Les brûlures
Le blessé de guerre
Secours en milieu périilleux
Le blessé par attentat terroriste
13/09/2019
Médecine et parachutisme dans les armées
12/09/2019
Ophtalmologie de guerre
16/04/2019
FST, chirurgie et USAparticulièrement innovant
TCCC: Un écosystème spécifique
Un regard sur l'émergence des nouvelles modalités de prise en charge des blessés de guerre avec pour point d'orgue l'innovation conduite et la construction d'un écosystème complet autour de la prise en charge du blessé de guerre. Une démarche à comprendre et à bien méditer.
Clic sur l'image pour accéder au document