01/10/2013
Infection in conflict wound
Infection in conflict wound
Eardley WGP et All. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B (2011) 366, 204–218
Although mechanisms of modern military wounding may be distinct from those of ancient conflicts, the infectious sequelae of ballistic trauma and the evolving microbial flora of war wounds remain a considerable burden on both the injured combatant and their deployed medical systems. Battlefieldsurgeons of ancient times favoured suppuration in war wounding and as such Galenic encouragement of pus formation would hinder progress in wound care for centuries. Napoleonic surgeonseventually abandoned this mantra, embracing radical surgical intervention, primarily by amputation, to prevent infection. Later, microscopy enabled identification of microorganisms and characterization of wound flora. Concurrent advances in sanitation and evacuation enabled improved outcomes and establishment of modern military medical systems. Advances in medical doctrine and technology afford those injured in current conflicts with increasing survivability through rapid evacuation, sophisticated resuscitation and timely surgical intervention. Infectious complications in those that do survive, however, are a major concern. Addressing antibiotic use, nosocomial transmission and infectious sequelae are a current clinical management and research priority and will remain so in an era characterized by a massive burden of combat extremity injury. This paper provides a review of infection in combat wounding from a historical setting through to the modern evidence base.
| Tags : infection
21/09/2013
Contamination des plaies: A l'entrée et la sortie
Effect of Initial Projectile Speed on Contamination Distribution in a Lower Extremity Surrogate “Wound Track”
Krebsbach MA et All., Military Medicine, 177, 5:573, 2012
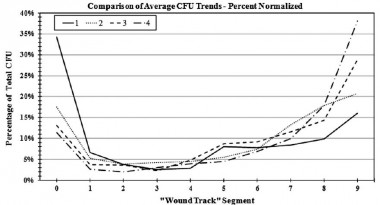
Le nettoyage précoce et la couverture des orifices d'entrée et de sortie sont donc théoriquement des maillons importants de la lutte contre l'infection des plaies de guerre.
| Tags : infection, balistique, pansement
27/08/2011
Prévention des infections des traumatisés de guerre
| Tags : infection
