15/02/2011
Intubation préhospitalière: Que penser de l'AIRTRAQ ?
Comme pour tout il faut s'entraîner et on n'inove pas. On rappelle que, en conditions de combat, le contrôle des voies aériennes a pour but essentiellemment de prévenir l'obstruction des voies aériennes, de prévenir l'inhalation du contenu gastrique. Le traitement d'une détresse respiratoire fait appel avant tout à l'oxygénothérapie si vous disposez d'oxygène, au traitement d'une cause spécifique (pneumo ou hémothorax, volet thoracique, plaie soufflante), à l'assistance ventilatoire au ballon par masque facial et EVENTUELLEMENT après intubation ou coniotomie sur une canule de 6 mm si les conditions tactiques le permettent.
Use of the Airtraq laryngoscope for emergency intubation in the prehospital setting: A randomized control trial
Trimmel H et all.
Crit Care Med 2011 Vol. 39, No. 3, 1-5
Objectives: The optical Airtraq laryngoscope (Prodol Meditec, Vizcaya, Spain) has been shown to have advantages when compared with direct laryngoscopy in difficult airway patients. Furthermore, it has been suggested that it is easy to use and handle even for inexperienced advanced life support providers. As such, we sought to assess whether the Airtraq may be a reliable alternative to conventional intubation when used in the prehospital setting.
Design, Setting, and Patients: Prospective, randomized control trial in emergency patients requiring endotracheal intubation provided by anesthesiologists or emergency physicians responding with an emergency medical service helicopter or ground unit associated with the Department of Anesthesiology, General Hospital, Wiener Neustadt, Austria.
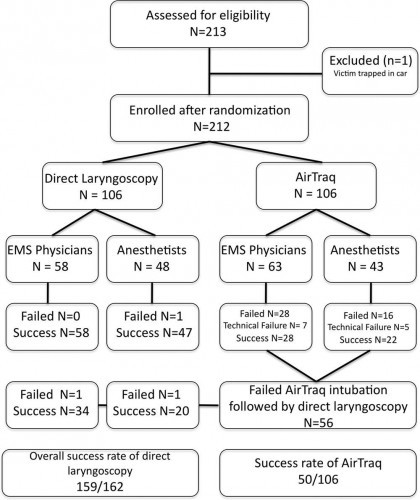
Measurements and Main Results: During the 18-month study period, 212 patients were enrolled. When the Airtraq was used as first-line airway device (n = 106) vs. direct laryngoscopy (n =106), success rate was 47% vs. 99%, respectively (p < .001). Reasons for failed Airtraq intubation were related to the fiberoptic characteristic of this device (i.e., impaired sight due to blood and vomitus, n = 11) or to assumed handling problems (i.e., cuff damage, tube misplacement, or inappropriate visualization of the glottis, n = 24). In 54 of 56 patients where Airtraq intubation failed, direct laryngoscopy was successful on the first attempt; in the remaining two and in one additional case of failed direct laryngoscopy, the airway was finally secured employing the Fastrach laryngeal mask. There was no correlation between success rates and body mass index, age, indication for airway management, emergency medical service unit, or experience of the physicians.
Conclusions: Based on these results, the use of the Airtraq laryngoscope as a primary airway device cannot be recommended in the prehospital setting without significant clinical experience obtained in the operation room. We conclude that the clinical learning process of the Airtraq laryngoscope is much longer than reported in the anesthesia literature.
| Tags : intubation, airway

Les commentaires sont fermés.