Et l'albumine ?
12/11/2015
Is limited prehospital resuscitation with plasma more beneficial than using a synthetic colloid? An experimental study in rabbits with parenchymal bleeding
Kheirabadi BS et Al. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015;78: 752-759
--------------------------------------
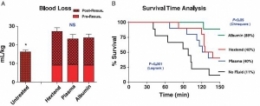
Il existe de grands débats sur la manière optimale d'assurer le remplissage vasculaire des blessés de guerre. Pour certains le fluide de référence est un hydroxyéthylamidon, pour d'autres un cristalloïde isotonique et en ce qui nous concerne les deux avec la mise en avant du sérum salé hypertonique premier suivi d'HEA. Actuellement il existe une tendance à promouvoir une autre stratégie faisant appel pour les blessés les plus graves au plasma voire la transfusion de sang frais. L'étude proposée avait pour objectif de confirmer l'intérêt d'une démarche "plasma premier". Une des surprises a été de constater que ce n'est pas cette dernière qui permettait d'obtenir le meilleur taux de survie mais l'emploi d'albumine, et ce de loin. Ces données expérimentales certes très partielles permettent aux auteurs (?) de rediscuter les conclusions de travaux anciens notamment de l'étude SAFE (1,2). Les solutés d'albumine utilisés par cette dernière ont une osmolarité de 260 mosm/kg (versus 305 mosm/kg pour le sérum salé). Les effets délétères notamment chez le traumatisé crânien pourraient être dus non pas à l'extravasation d'albumine dans le parenchyme cérébral lésé mais à l'hypoosmolarité de l'albumex 4%, ces deux mécanismes concourrant à la plus grande fréquence d'HTIC dans le groupe albumine (3). A méditer
--------------------------------------
BACKGROUND:
Reports of survival benefits of early transfusion of plasma with red blood cells (1:1 ratio) in trauma patients suggest that plasma may be a better fluid to replace Hextend for battlefield resuscitation. We studied possible advantages of prehospital resuscitation with plasma compared with Hextend or albumin in a model of uncontrolled hemorrhage.
METHODS:
Male New Zealand white rabbits (3.3 T 0.1 kg) were anesthetized, instrumented, and subjected to a splenic injury with uncontrolled bleeding. Ten minutes after injury (mean arterial pressure [MAP] G 40 mm Hg), the rabbits received small and equal volumes (15 mL/kg) of rabbit plasma (n = 10), Hextend (n = 10), or 5% human albumin (n = 9) or no fluid. Fluids were administered in two bolus injections (20 minutes apart) and targeted to aMAP of 65 mm Hg. Animals were monitored for 2.5 hours or until death, and their blood losses were measured. Arterial blood samples were collected at different times and analyzed for ABG, CBC, and coagulation tests.
RESULTS:
There were no differences in baseline measures among groups. Splenic injury caused similar hemorrhages (9.1 T 0.4 mL/kg at 10 minutes) and decreased MAP in all subjects. Subsequent resuscitation initiated additional bleeding. At 60 minutes after injury (20 minutes after resuscitation), longer activated partial thromboplastin time and lower fibrinogen concentrations were apparent compared with baseline values with differences among groups. Thrombelastography analysis indicated faster and stronger clot formation with plasma and albumin resuscitation than with Hextend use. Shock indices were increased in all groups, but smaller changes were measured in the albumin group. Total blood loss did not differ among resuscitated rabbits but was higher (p G 0.05) than among nonresuscitated animals. Survival rates were 11% (untreated), 40% (Hextend and plasma), and 89% (albumin, p G 0.05).
CONCLUSION:
Resuscitation with plasma or albumin better preserved coagulation function than did Hextend. However, despite these improvements, plasma resuscitation did not reduce blood loss or improve survival, while albumin administration seemed beneficial


Les commentaires sont fermés.