20/11/2025
Chaine de survie 21ème siècle: Réflexions US
Clic sur l'image pour accéder au document
Le facteur humain reste CENTRAL
"While technology continues to transform warfare, the human element remains central to military medicine. The operational ‘kill chain’ may be accelerated by drones and artificial intelligence. However, the medical ‘survival chain’ still demands human judgement, compassion, and moral courage"
01/12/2022
Facteurs humains en situations critiques
08/06/2022
Trauma Prehospitalier: Aides
| Tags : traumatologie
01/10/2019
Préparation mentale: Soyez pratiquants +++
Mental Skills in Surgery: Lessons Learned from Virtuosos, Olympians, and Navy Seals.
----------------------------------------
Les techniques de préparation mentale ont fait leurs preuves dans le domaine du sport. Elles commencent à être utilisées dans le domaine médical ET CELA MARCHE. Le document proposé fait le point sur son intérêt.
----------------------------------------
OBJECTIVE:
The present study investigated the role of mental skills in surgery through the unique lens of current surgeons who had previously served as Olympic athletes, elite musicians, or expert military personnel.
BACKGROUND:
Recent work has demonstrated great potential for mental skills training in surgery. However, as a field, we lag far behind other high-performance domains that explicitly train and practice mental skills to promote optimal performance. Surgery stands to benefit from this work. First, there is a need to identify which mental skills might be most useful in surgery and how they might be best employed.
METHODS:
Using a constructivist grounded theory approach, semi-structured interviews were conducted with 17 surgeons across the United States and Canada who had previously performed at an elite level in sport, music, or the military.
RESULTS:
Mental skills were used both to optimize performance in the moment and longitudinally. In the moment, skills were used proactively to enter an ideal performance state, and responsively to address unwanted thoughts or emotions to re-enter an acceptable performance zone. Longitudinally, participants used skills to build expertise and maintain wellness.
CONCLUSIONS:
Establishing a taxonomy for mental skills in surgery may help in the development of robust mental skills training programs to promote optimal surgeon wellness and performance.
21/12/2017
Préparateur sportif et trauma sévère: Une évidence !
Cocks M et Al. J Surg Educ. 2014 Mar-Apr;71(2):262-9
BACKGROUND:
Mental practice has been successfully applied in professional sports for skills acquisition and performance enhancement. The goals of this review are to describe the literature on mental practice within sport psychology and surgery and to explore how the specific principles of mental practice can be applied to the improvement of surgical performance-both in novice and expert surgeons.
METHOD:
The authors reviewed the sports psychology, education, and surgery literatures through Medline, PubMed, PsycINFO, and Embase.
RESULTS:
In sports, mental practice is a valuable tool for optimizing existing motor skill sets once core competencies have been mastered. These techniques have been shown to be more advantageous when used by elite athletes. Within surgery, mental practice studies have focused on skill acquisition among novices with little study of how expert surgeons use it to optimize surgical preparation.
CONCLUSIONS:
We propose that performance optimization and skills acquisition should be viewed as 2 separate domains of mentalpractice. Further understanding of this phenomenon has implications for changing how we teach and train not only novice surgeons but also how experienced surgeons continue to maintain their skills, acquire new ones, and excel in surgery.
| Tags : top
26/06/2013
Facteurs humains: Les prendre en compte pour votre préparation
Lessons from the battlefield: human factors in defence anaesthesia
Mercer SJ et All. BJA 105 (1): 9–20 (2010)
Ce document insiste sur l'importance des factuers humains sur la performance des équipes d'anesthésistes déployés dans un environnement peu familier, des situations beaucoup plus complexes que celles rencontrées dans leur pratique habituelle. Il insiste sur les phases de préparation en amont sur des scenarii proches de ceux rencontrés en réels et sur les moyens de condurie cette préparation notamment le recours à la simulation haute fidélité.
31/05/2013
Mieux on est formé, plus on fait
Army flight medic performance of paramedic level procedures: Indicated vs performed
Bier SA et all. - J Emerg Med. 2013 May;44(5):962-9.
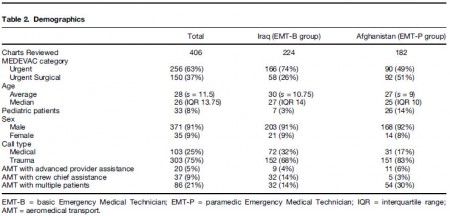
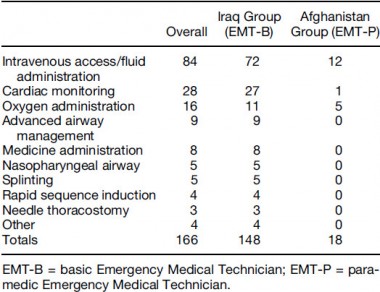
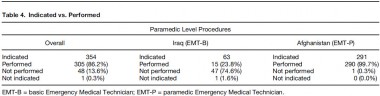
Of 984 interventions found to be indicated on the 406 charts that met inclusion criteria, 36% were rated as EMT-P level. Seventeen percent were indicated but not performed. EMT-Bs failed to perform indicated procedures 35% of the time vs. 3% in the EMT-P group (p < 0.001). For paramedic-level procedures, EMTBs failed to make 76% of appropriate interventions, compared to <1% in the EMT-P group (p < 0.001). Conclusions: There seems to be a substantial number of procedures beyond the scope of standard Army flight medic training being required for Army AMT missions. It seems that when advance interventions are indicated, those trained to the EMT-P level perform them significantly more often than those trained to Army standard. Conclusions: Based on the findings of this study, the authors suggest the Army consider adopting the standards required for civilian AMT
Commentaire:Notez la part de pédiatrie
Commentaire: EMT-B = Auxilaire sanitaire. EMT P = Technicien de niveau plutôt infirmiers formés exclusivement à la gestion de soins critiques. Pas d'équivalence avec la vision française (entre infirmier anesthésiste/réa ?)
Ceci milite pour la présence dans les vecteurs d'EVASAN notamment aériens de personnels paramédicaux spécifiques habitués à la mise en oeuvre de standards de soins critiques
| Tags : evasan