11/11/2016
15 ans d'emploi du tourniquet: Que dire ?
Battlefield Tourniquets: Lessons Learned in Moving Current Care Toward Best Care in an Army Medical Department at War
Kragh JF Jr et Al. US Army Med Dep J. 2016 Apr-Sep;(2-16):29-36.
------------------------------
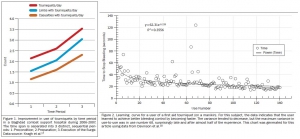
Un point d'étape qui insiste sans surprise sur l'apport d'une pose précoce d'un garrot. Précoce mais aussi rapide: 25 secondes sont nécessaires aux plus entraînés mais c'est 20 secondes de trop. Plus on s'entraîne et plus vite ET mieux on pose ce garrot.
------------------------------
Bleeding prevention and control by tourniquet use by out-of-hospital caregivers is a major breakthrough in military medicine of current wars. The present review documents developments in tourniquet practices since 2001 among the US military services for aid in improving doctrine, policy, and especially care in wars to come. Tourniquets are an adjunct for resuscitation in self-care and buddy aid and today are issued to all military service persons who deploy into a combat zone. In the US Army, virtually every Soldier is trained in first aid tourniquet use; since 2009 they are instructed early and often to use them early and often. Despite substantial knowledge gains among the services in tourniquet use and resulting improvements in casualty survival, current evidence shows persistent diffi culties in achieving best care with tourniquet use for individual trauma patients. Nevertheless, contemporary tourniquet use incorporates key lessons learned over the last 14 years of war that include: (1) tourniquet use reliably stops bleeding from limb wounds and prevents mortality in prehospital settings; and (2) brief tourniquet use appears to be safe. These 2 lessons have become so evident that civilian emergency medical systems have begun using them, albeit unevenly. Collection and interpretation of data of casualties with tourniquet use have showed that such intervention has lifesaving benefit through 2 mechanisms: control of both ongoing hemorrhage and shock severity. The next generation of interventions in bleeding control involves developing the skill sets, education, and standards of tourniquet users which may improve hemorrhage control in wars to come
| Tags : tourniquet

Les commentaires sont fermés.