13/05/2014
Lésions rachidiennes: Plus fréquentes qu'envisagé
Spinal Injuries in United States Military Personnel Deployed to Iraq and Afghanistan
An Epidemiological Investigation Involving 7877 Combat Casualties From 2005 to 2009
Schoenfeld AJ et All. Spine 2013;38:1770–1778
Les lésions du rachis sont plus fréquentes que ce qui était supposé. Ce travail rapporte qu'une atteinte du rachis est présente dans 11% des cas. Une des explications est que l'amélioration des conditions de prise en charge permet la survie de blessés plus graves qu'auparavant, qui autrefois ne survivait pas à leurs blessures.
-----------------------------------------------------------
In the years 2005 to 2009, 872 (11.1%) casualties with spine injuries were identified among a total of 7877 combat wounded. The mean age of spine casualties was 26.6 years. Spine fractures were the most common injury morphology, comprising 83% of all spinal wounds. The incidence of combat-related spinal trauma was 4.4 per 10,000, whereas that of spine fractures was 4.0 per 10,000. Spinal cord injuries occurred at a rate of 4.0 per 100,000.
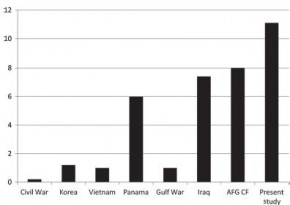
Spinal cord injuries were most likely to occur in Afghanistan (incident rate ratio: 1.96; 95% confi dence interval: 1.68–2.28), among Army personnel (incident rate ratio: 16.85; 95% confidence interval: 8.39–33.84), and in the year 2007 (incident rate ratio: 1.90; 95% confi dence interval: 1.55–2.32). Spinal injuries from gunshot were significantly more likely to occur in Iraq (17%) than in Afghanistan (10%, P = 0.02).
-----------------------------------------------------------
| Tags : rachis

Les commentaires sont fermés.