03/12/2011
Médecine et Armées
Rachis: Immobilisation et traumatismes pénétrants, que dit le PHTLS ?
Prehospital Spine Immobilization for Penetrating Trauma—Review
and Recommendations From the Prehospital Trauma Life Support
Executive Committe
http://www.ucdmc.ucdavis.edu/emergency/education/residenc...
- There are no data to support routine spine immobilization in patients with penetrating trauma to the neck or torso.
- There are no data to support routine spine immobilization in patients with isolated penetrating trauma to the cranium.
- Spine immobilization should never be done at the expense of accurate physical examination or identification and correction of life-threatening conditions in patients with penetrating trauma.
- Spinal immobilization may be performed after penetrating injury when a focal neurologic deficit is noted on physical examination although there is little evidence of benefit even in these cases.
ATTENTION
Le PHTLS, qui correspond à un ensemble de procédures destinée à être mises en oeuvre par des techniciens d'urgence, ne reflète pas du tout la pratique française.
02/12/2011
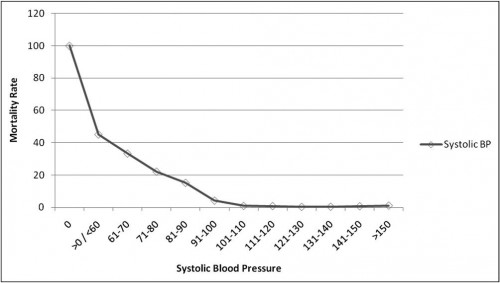
Plus de mortalité si la PA est inférieure à 100 mmHg
Hypotension is 100 mm Hg on the battlefield.
Eastridge BJ et all. Am J Surg. 2011 Oct;202(4):404-8.
BACKGROUND:
Historically, emergency physicians and trauma surgeons have referred to a systolic blood pressure (SBP) of 90 mm Hg as hypotension. Recent evidence from the civilian trauma literature suggests that 110 mm Hg may be more appropriate based on associated acidosis and outcome measures. In this analysis, we sought to determine the relationship between SBP, hypoperfusion, and mortality in the combat casualty.
METHODS:
A total of 7,180 US military combat casualties from the Joint Theater Trauma Registry from 2002 to 2009 were analyzed with respect to admission SBP, base deficit, and mortality. Base deficit, as a measure of hypoperfusion, and mortality were plotted against 10-mm Hg increments in admission SBP.
RESULTS:
By plotting SBP, baseline mortality was less than 2% down to a level of 101 to 110 mm Hg, at which point the slope of the curve increased dramatically to a mortality rate of 45.1% in casualties with an SBP of 60 mm Hg or less but more than 0 mm Hg. A presenting SBP of 0 mm Hg was associated with 100% mortality. The data also established a similar effect for base deficit with a sharp increase in the rate of acidosis, which became manifest at an SBP in the range of 90 to 100 mm Hg.
CONCLUSIONS:
This analysis shows that an SBP of 100 mm Hg or less may be a better and more clinically relevant definition of hypotension and impending hypoperfusion in the combat casualty. One utility of this analysis may be the more expeditious identification of battlefield casualties in need of life-saving interventions such as the need for blood or surgical intervention.
-----------------------------
Une PAS de moins de 100 mmHg est un facteur de mortalité chez le blessé. La procédure de sauvetage au combat indique la nécessité de préserver un pouls radial perceptible associée à une conscience normale. Il s'agit donc d'un impératif absolu car ces deux éléments sont chez le blessé au combat hémorragique obtenu par la mise en jeu de mécanismes compensateurs contre lesquels le temps joue.