Amputé des jambes: Le bassin aussi !
19/12/2015
The incidence of pelvic fractures with traumatic lower limb amputation in modern warfare due to improvised explosive devices
Cross AM et Al. J R Nav Med Serv 2014;100(2):152-6
---------------------------------------------
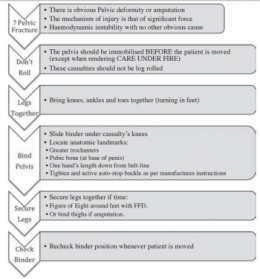
Excepté l'extraction d'urgence de blessés sous le feu, la prise en charge den cas d'amputation traumatique doit inclure la forte probabilité de traumatisme du bassin. Une utilisation large des immobilisations pelviennes doit donc être à l'esprit. On rappelle simplement la gravité et la difficulté de prise en charge des hémorragies liées aux fractures de bassin.
---------------------------------------------
AIMS:
A frequently-seen injury pattern in current military experience is traumatic lower limb amputation as a result of improvised explosive devices (IEDs). This injury can coexist with fractures involving the pelvic ring. This study aims to assess the frequency of concomitant pelvic fracture in IED-related lower limb amputation.
METHODS:
A retrospective analysis of the trauma charts, medical notes, and digital imaging was undertaken for all patients arriving at the Emergency Department at the UK military field hospital in Camp Bastion, Afghanistan, with a traumatic lower limb amputation in the six months between September 2009 and April 2010, in order to determine the incidence of associated pelvic ring fractures.
RESULTS:
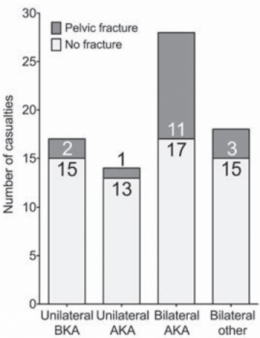
Of 77 consecutive patients with traumatic lower limb amputations, 17 (22%) had an associated pelvic fracture (eleven with displaced pelvic ring fractures, five undisplaced fractures and one acetabular fracture). Unilateral amputees (n = 31) had a 10% incidence of associated pelvic fracture, whilst 30 % of bilateral amputees (n = 46) had a concurrent pelvic fracture. However, in bilateral, trans-femoral amputations (n = 28) the incidence of pelvic fracture was 39%.
CONCLUSIONS:
The study demonstrates a high incidence of pelvic fractures in patients with traumatic lower limb amputations, supporting the routine pre-hospital application of pelvic binders in this patient group


Les commentaires sont fermés.