Mieux on est formé, plus on fait
31/05/2013
Army flight medic performance of paramedic level procedures: Indicated vs performed
Bier SA et all. - J Emerg Med. 2013 May;44(5):962-9.
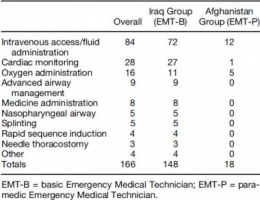
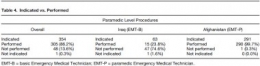
Of 984 interventions found to be indicated on the 406 charts that met inclusion criteria, 36% were rated as EMT-P level. Seventeen percent were indicated but not performed. EMT-Bs failed to perform indicated procedures 35% of the time vs. 3% in the EMT-P group (p < 0.001). For paramedic-level procedures, EMTBs failed to make 76% of appropriate interventions, compared to <1% in the EMT-P group (p < 0.001). Conclusions: There seems to be a substantial number of procedures beyond the scope of standard Army flight medic training being required for Army AMT missions. It seems that when advance interventions are indicated, those trained to the EMT-P level perform them significantly more often than those trained to Army standard. Conclusions: Based on the findings of this study, the authors suggest the Army consider adopting the standards required for civilian AMT
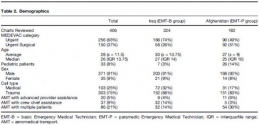
Commentaire:Notez la part de pédiatrie
Commentaire: EMT-B = Auxilaire sanitaire. EMT P = Technicien de niveau plutôt infirmiers formés exclusivement à la gestion de soins critiques. Pas d'équivalence avec la vision française (entre infirmier anesthésiste/réa ?)
Ceci milite pour la présence dans les vecteurs d'EVASAN notamment aériens de personnels paramédicaux spécifiques habitués à la mise en oeuvre de standards de soins critiques


Les commentaires sont fermés.