02/05/2015
Haute fidélité: Utile ? Pas si sûr
The use of high-fidelity manikins for advanced life support training. A systematic review and meta-analysis
Cheng A et All. Resuscitation. 2015 Apr 14. pii: S0300-9572(15)00152-5
---------------------------------------------------------
Le recours à la simulation apparaît incontournable en pédagogie médicale. L'emploi de mannequins haute fidélité connait un essort majeur. Si la satisfaction des étudiants semble au rendez-vous, il n'est cependant pas si évident que la simulation haute fidélité soit dimensionnante en terme d'acquisition réelle de savoir faire. Les avis sont partagés. Ainsi C'est travail évoque un niveau de preuve relativement faible voir absent. Compte tenu du coût non négligeable des mannequins haute fidélité, un tel investissement doit donc être réfléchi.
--------------------------------------------------------
Objectives:
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of high versus low fidelity manikins in the context of advanced life support training for improving knowledge, skill performance at course conclusion, skill performance between course conclusion and one year, skill performance at one year,skill performance in actual resuscitations, and patient outcomes.
Methods:
A systematic search of Pubmed, Embase and Cochrane databases was conducted through January31, 2014. We included two-group non-randomized and randomized studies in any language comparing high versus low fidelity manikins for advanced life support training. Reviewers worked in duplicate to extract data on learners, study design, and outcomes. The GRADE (Grades of Recommendation, Assess-ment, Development and Evaluation) approach was used to evaluate the overall quality of evidence foreach outcome.
Results: 3840 papers were identified from the literature search of which 14 were included (13 randomized controlled trials; 1 non-randomized controlled trial). Meta-analysis of studies reporting skill performanceat course conclusion demonstrated a moderate benefit for high fidelity manikins when compared withlow fidelity manikins [Standardized Mean Difference 0.59; 95% CI 0.13–1.05]. Studies measuring skill performance at one year, skill performance between course conclusion and one year, and knowledge demonstrated no significant benefit for high fidelity manikins
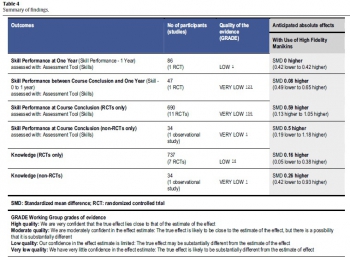
Conclusion:
The use of high fidelity manikins for advanced life support training is associated with moderate benefits for improving skills performance at course conclusion. Future research should definethe optimal means of tailoring fidelity to enhance short and long term educational goals and clinical outcomes.
| Tags : simulateurs

Les commentaires sont fermés.